Basic Web Design with HTML and CSS
A web
page or webpage is a document, commonly written
in HTML, that is viewed in an Internet browser. A web page can be accessed by
entering a URL address into a browser's address
bar. A
web page may contain text, graphics, and hyperlinks to other web pages and files.
WebSite: A website is a
collection of several web pages. These pages are linked together with
hyperlinks. A website has a unique domain name, and we can access it by
entering that domain name in the URL.
A domain name is a string of characters that identifies a website. It
is what users type in their browser to visit your site.
Web hosting is a service that provides space on a server for your
website files, allowing it to be available on the internet. When visitors
access your domain name, the hosting provider will transfer those files to
their web browsers.
Two types of website
|
Static website |
Dynamic Website |
|
A Static Website (sometimes called a
flat or stationary page) is displayed in a web browser exactly as it is
stored. It contains web pages with fixed content coded in HTML and stored on
a web server. It does not change, it stays the same, or "static"
for every viewer of the site. |
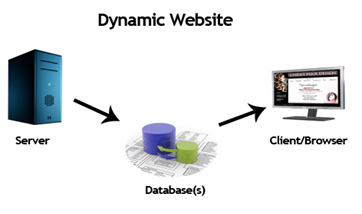
A dynamic website (also referred to as a database-driven
site) contains information and content that changes, depending on factors
such as the viewer of the site, the time of the day, the time zone, or the
native language of the country the viewer). The content of your site
(text/images) is stored on a database or content management system. When
the information is updated or changed within the database, it changes on the
site. |
|
Using simple languages such as HTML, CSS, or JavaScript. |
A Dynamic Website requires web
programming and database design. (PHP, ASP.NET, Node.js etc.) |
|
|
|
Search Engine: A search engine is
an internet service that helps users find any information available on the
internet. Some examples of search engines are Google, Yahoo, Bing,
DuckDuckGo, Ask.com, AOL, Baidu It is usually accessed with the help
of Web browser.
Web Browser: A web browser or
simply browser is application software used to access the internet. Some examples
of Web browsers are Google Chrome, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Safari,
etc. It does two things:
It connects to a web server on the internet and
requests a page that the user wants to view; once it finds that page, it
displays it on its device.
It can interpret the set of HTML tags within a
page to display the page in the correct format.
Webserver: A web server can
be understood as a computer that hosts or provide a website on the internet. It
contains webserver software and component files of a website such as HTML
document, images, CSS stylesheet, and JS files.
web development framework (WDF)
A web development framework is a set of
resources and tools for software developers to build and manage web
applications, web services and websites.
Difference between website and web application
Interactivity
|
The first point to start ‘web
application vs. website’ differentiation with is interactivity. A website
provides visual and text content that the user can see and read, but not
affect in any way. In the case of a web application, the user can not only read
the page content but also manipulate the data on this page. The interaction
takes the form of a dialog: the user clicks a button or submits a form and
gets a response from the page. This response may take a form of a document
download, online chat, electronic payment and more. |
|
Integration |
Integration
means bringing together different components to build a more comprehensive
system. Both websites and web applications can be integrated with other
software (CRM, ERP, etc.). Still, integration is more typical for web
applications, because their complex functionality often requires interaction
with extra systems. Take
integration of a business web application (say, an e-shop) with a CRM
(Customer Relationship Management) system. A CRM stores all customer data in
one place, providing easy access to them for the employees. The integration
will allow automatic collection of web application user data and storing it
in the CRM. This way, your team will get access to a full set of data about
customers, their inquiries, communication, and feedback. This enables
exploring customer behavior and buying habits, as well as settle their claims
faster. Moreover, any change in customer data will be reflected in the CRM
instantly. Always staying up to date with your customer preferences, you will
reduce churn rates and increase sales. A
website also can be integrated with a CRM. This allows providing users with
more personalized content. However, for a website, it’s rather a rarely
implemented feature than a part of the core functionality. |
|
Authentication |
Authentication
is the procedure that involves entering a user’s login and password to get
access to the system. It is a must for the web software that requires any
personal information. User accounts must be secured to prevent unauthorized
access and leakage of sensitive data. Web
applications mostly require authentication, as they offer a much broader
scope of options than websites. Consider an example of social networks. When
you register, you create an account and get a unique identification number.
The system warns you if your login and password are weak. If you leave them
unchanged, hackers may reach your account and steal your information, as well
as irritate other users with junk emails under your name. Authentication
is not obligatory for informational websites. The user may be offered to
register to get access to additional options unavailable to unregistered
website visitors. For example, you may look through news and featured
articles on a news website without bothering to register. However, if you
want to leave a comment you will have to log in. This way, users confirm
their identity allowing the system to block spammers. As
you can see, both websites and web applications may require authentication.
However, for web applications, it is obligatory due to security reasons. |
What is Web
Design?
Web design consists of
the design of a digital product (websites and apps). It may encompass
several fields, such as User Interface (UI), User Experience (UX),
and even Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Overall, web design must
acknowledge the usability of a website or app, considering its layout
(i.e., the structure), visual aesthetics (e.g., colors and fonts), and
sometimes the content.
Responsive Web Design
Responsive web design makes your web page look
good on all devices. Responsive web design uses only HTML and CSS. Responsive web
design is not a program or a JavaScript.
Web pages should not leave out information to fit
smaller devices, but rather adapt its content to fit any device:
What
is Web Development?
Web Development is
the process of developing websites and applications for the internet or
intranets (private networks). As a process, web development can include
various specializations, such as working on the webserver, web engineering,
network security configuration, and even web design. However, the everyday use of the term "web
development" typically refers to coding or writing markups and does not
often include design aspects.
There are three types of developers:
back-end, front-end, and full-stack.
The back-end developer is
responsible for the server-side and for everything that communicates between
the database and the browser;
The front-end developer is the
one working on the client-side of software development, thus focusing on how
users see the product;
Most Commonly Used
Languages
·
HTML - HyperText Markup Language
·
CSS - Cascading Style Sheets
·
JavaScript
·
SQL - Structured Query Language
·
PHP - Hypertext Preprocessor
·
Java
·
Python
·
.NET
·
Angular
EDITOR
1. Notepad ++
2.
Atom
4. Dreamweaver
The <HTML> is a markup language
that is used by the browser to manipulate text, images, and other content to
display it in the required format.
Html inventor : Tim
Berners-Lee in 1993
Latest version : HTML 5.0 which was
published in the year 2012
Why Learn HTML?
HTML
is the foundation of all web pages. Without HTML, you wouldn’t be able to organize
text or add images or videos to your web pages. HTML is the beginning of
everything you need to know to create engaging web pages!
Is HTML a programming language?
HTML
is called as a markup language that is different from a programming
language. Its full form is Hypertext Markup Language.
Hyper Text: Hypertext
simply means "Text within Text." A text has a link within it, is a
hypertext. Whenever you click on a link which brings you to a new webpage, you
have clicked on a hypertext. Hypertext is a way to link two or more web pages
(HTML documents) with each other.
Markup language: A markup language is a computer language that is used
to apply layout and formatting conventions to a text document. Markup language
makes text more interactive and dynamic. It can turn text into images, tables,
links, etc.
In
conclusion, HTML is not a
programming language. A programming language uses logic to produce a result, it
uses conditional statements, variables, functions, etc. Whereas HTML is a
markup language, that create structures using tags for the data presentation.
There is no logic or algorithm involved.
Tags in HTML: Tags are one of the most important part in an HTML
Document. HTML uses some predefined tags which tells the browser about content
display property, that is how to display a particular given content.
For Example,
to create a paragraph, one must use the paragraph tags(<p> </p>)
and to insert an image one must use the img tags(<img />).
There are generally two types of tags in HTML:
1. Paired/opening
and closing Tags: These tags come in pairs. That is they have both opening
(< >) and closing(</ >) tags.
2. Null/Empty/Singular
Tags: These tags do not require to be closed.
List of some paired tags in HTML:
Some Unpaired Tags are:
HTML Structure
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>: Doctype
stands for Document Type Declaration. It informs the web browser about the
type and version of HTML used in building the web document. This helps the
browser to handle and load it properly.
<html>: This
is called HTML root element and used to wrap all the code.
<head>: Head
tag contains metadata, title, page CSS etc. All the HTML elements that can be
used inside the <head> element are:
<body>: Body
tag is used to enclose all the data which a web page has from texts to links.
All the content that you see rendered in the browser is contained within this
element.
Printing Hello World
Open your text editor, and type the below code in it
and save it with the name “index.html”.
Note: HTML files are saved with the file extension .html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> </title>
</head>
<body>
Hello World!
</body>
</html>
Output: On opening the
file in a web browser, you will see the below output.
Background Color in HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> </title>
</head>
<body
style="background-color:powderblue;" >
Hello World!
</body>
</html>
Some Color code in html
https://www.w3schools.com/html/html_colors_hex.asp
Heading Tags:
There are six levels of headings defined by HTML. These six heading elements
are h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, and h6; with h1 being the highest level and h6 the
least.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
First Web Page
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<h2>Hello World!</h2>
<h3>Hello World!</h3>
<h4>Hello World!</h4>
<h5>Hello World!</h5>
<h6>Hello World!</h6>
</body>
</html>
|
HTML element |
rank |
example text |
pixel height |
|
<h1> </h1> |
1 |
h1
|
32
px |
|
<h2> </h2> |
2 |
h2
|
24
px |
|
<h3> </h3> |
3 |
h3
|
18.72
px |
|
<h4> </h4> |
4 |
h4
|
16
px |
|
<h5> </h5> |
5 |
h5
|
13.28
px |
|
<h6> </h6> |
6 |
h6
|
10.72
px |
Syntax of HTML Comments :
<!--
Write your comments here -->
Define Some TAG
<b>This
text is bold</b> <br>
<em>This
text is emphasize</em><br><!--emphasize
-->
<u>This
text with underline</u><br><!--underline -->
<small>This
text with small font</small><br><!--small font -->
<big>This
text is big font</big><br><!--big
font -->
<strong>strong
text</strong><br><!-- strong text
-->
<mark>hilight
text</mark><br><!-- hilight text
-->
<b>H<sub>2</sub>O, A<sup>2</sup></b><br>
<hr
width="100%" size="5" color="red">
<abbr
title="Worl Wide Web">WWW</abbr><br><!--abbreviation-->
<p> use
br tag for line break </p></br><!—paragraph-->
<pre> preformatted
text which preserves the text
spaces, line breaks, tabs, and other formatting characters </pre>
<!-- preformatted
text - ->
<q>represent
with quation inside text</q> </br><!-- represent with quation ->
<del>
draw a line throw a text</del> </br>
Work with Table in html
<table>
<tr>
<td>Month</td>
<td>Savings</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
</table>
Table
Height width and border
<table
align="center" width=500, height=500 border=2>
<tr>
<tr>Month</tr>
<tr>Savings</tr>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
</table>
Table
Content Align
Put
this code into head section
<style>
table, td, th {
border: 1px solid
black;
}
table {
border-collapse:
collapse;
width: 100%;
}
td {
text-align:
center; <!- - horizontal align: center, left, right-->
}
td {
vertical-align: bottom;
<!- - Vertical align: bottom, top, middle -->
}
</style>
Table
Heading and caption
<table align="center" width=500, height=500
border=2>
<caption
style="caption-side:bottom">My savings</caption>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
</table>
Table
background Using inline CSS
<table
style="background-color:pink;">
<tr
style="background-color:gray;color:red;">
<th>Table
Header</th><th>Table Header</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Table cell
1</td><td>Table cell 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Table cell
3</td><td>Table cell 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
Table
background Using internal CSS Classes
<!-- Start Styles. Move the 'style' tags and everything between them
to between the 'head' tags -->
<style type="text/css">
.myTable { background-color:#eee;border-collapse:collapse; }
.myTable th { background-color:#000;color:white;width:50%; }
.myTable td, .myTable th { padding:5px;border:1px solid #000; }
</style>
<!-- End Styles -->
<table class="myTable">
<tr>
<th>Table Header</th>
<th>Table Header</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Table cell 1</td>
<td>Table cell 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Table cell 3</td><td>Table cell 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
HTML Table Colspan
& Rowspan
|
<!DOCTYPE
html> <html> <head> <style> table, th, td { border: 1px solid black; border-collapse: collapse; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Cell
that spans two rows</h2> <p>To make
a cell span more than one row, use the rowspan attribute.</p> <table
style="width:100%"> <tr> <th>Name</th> <td>Jill</td> </tr> <tr> <th
rowspan="2">Phone</th> <td>555-1234</td> </tr> <tr> <td>555-8745</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html> |
|
|
|
<!DOCTYPE
html> <html> <head> <style> table, th, td { border: 1px solid black; border-collapse: collapse; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Cell
that spans two columns</h2> <p>To make
a cell span more than one column, use the colspan attribute.</p> <table
style="width:100%"> <tr> <th
colspan="2">Name</th> <th>Age</th> </tr> <tr> <td>Jill</td> <td>Smith</td> <td>43</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Eve</td> <td>Jackson</td> <td>57</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html> |
|
|
HTML Images Syntax
The
HTML <img> tag
is used to embed an image in a web page.
The <img> tag
has two required attributes:
- src - Specifies
the path to the image
- alt - Specifies
an alternate text for the image
Syntax
<img src="url" alt="alternatetext">
Image tag
with style
<img src="img_girl.jpg" alt="Girl in a jacket"
style="width:500px;height:600px;">
Images in Another Folder
<img src="/images/html5.gif" alt="HTML5
Icon" style="width:128px;height:128px;">
Image as a Link
To
use an image as a link, put the <img> tag inside the <a> tag:
<a href="default.asp">
<img src="smiley.gif" alt="HTML
tutorial" style="width:42px;height:42px;">
</a>
HTML Lists
HTML lists allow web developers to group a set of related
items in lists.
Unordered HTML List
An unordered list starts with the <ul> tag.
Each list item starts with the <li> tag.
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
////////////
<ul style="list-style-type:disc;"><!—disc, circle,
square, none -->
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
Nested HTML Lists
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea
<ul>
<li>Black tea</li>
<li>Green tea</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
Ordered HTML List
An ordered list starts with the <ol> tag.
Each list item starts with the <li> tag.
<ol>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
/////////////////////
<ol type="1"> <!-- type=a,A,i,I,1
- ->
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
//////////control start
<ol type="1" start=3> <!--
type=a,A,i,I,1 - ->
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
HTML Description Lists
A description list is a list of terms, with a description of each
term.
<dl>
<dt>Coffee</dt>
<dd>- black hot drink</dd>
<dt>Milk</dt>
<dd>- white cold drink</dd>
</dl>
- Use
the HTML <dl> element to define a description list
- Use
the HTML <dt> element to define the description term
- Use
the HTML <dd> element to describe the term in a description
list
HTML Links - Hyperlinks
HTML links are hyperlinks.
You can click on a link and jump to another document.
When you move the mouse over a link, the mouse arrow
will turn into a little hand.
HTML Links – Syntax
<a href="url">link text</a>
////////////////////////////
<h2>Absolute URLs</h2>
<p><a href="https://www.w3.org/">W3C</a></p>
<p><a href="https://www.google.com/">Google</a></p>
<h2>Relative URLs</h2>
<p><a href="html_images.asp">HTML Images</a></p>
<p><a
href="test.html">CSS Tutorial</a></p> <!—file in same folder -->
<p><a
href="./ttt/student_form.html">CSS Tutorial</a></p> <!—file
in different folder -->
//////////////////////// put in head section for
different style of link
<style>
a:link {
color: green;
background-color: transparent;
text-decoration: none;
}
a:visited {
color: pink;
background-color: transparent;
text-decoration: none;
}
a:hover {
color: red;
background-color: transparent;
text-decoration: underline;
}
a:active {
color: yellow;
background-color: transparent;
text-decoration: underline;
}
</style>
//////////////////////////////
The Marquee Tag
The <marquee> tag is a container tag of HTML is implemented for
creating scrollable text or images within a web page from either left to right
or vice versa, or top to bottom or vice versa. But this tag has been deprecated in the new version of HTML,
i.e., HTML 5.
<marquee behavior="scroll" direction="up"
scrollamount="1">Slow Scrolling</marquee>
<marquee behavior="Alternate" direction="right" scrollamount="12">Alternate</marquee>
<marquee behavior="scroll" direction="left"
scrollamount="20">Fast Scrolling</marquee>
<marquee behavior="scroll" direction="right" scrollamount="50">Very Fast scrolling</marquee>
<audio controls>
<source src="audio-file.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>
Add Video
<video width="640" height="360" controls>
<source src="video-file.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
Optional Attributes
You can also add:
-
autoplay– Starts playing automatically -
loop– Plays again after finishing -
muted– Starts with no sound
1. <header>
- Represents
the introductory content or navigation links of a page or
section.
- Can
contain logo, title, navigation, etc.
- Can
appear multiple times (e.g., per section).
<header>
<h1>My
Website</h1>
<nav>
<a href="#home">Home</a>
<a
href="#about">About</a>
</nav>
</header>
2. <footer>
- Represents
the footer for a page or section.
- Typically
contains copyright, contact info, links, etc.
- Like
<header>, it can be used multiple times.
<footer>
<p>©
2025 My Website. All rights reserved.</p>
</footer>
3. <section>
- Defines
a thematic group of content, usually with a heading.
- Used
to split content into logical parts (e.g., chapters, tabs, topics).
<section>
<h2>About
Us</h2>
<p>We provide
tech education to students.</p>
</section>
4. <nav>
- Represents
a navigation section that links to other pages or parts of the
page.
- Usually
used inside <header> or elsewhere as needed.
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a
href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a
href="#services">Services</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Flexbox Webpage Layout</title>
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
min-height: 100vh;
}
header, footer {
background-color: #333;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
background-color: #444;
padding: 15px;
color: white;
}
color: white;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 15px;
}
display: flex;
flex: 1;
}
.sidebar {
flex: 1;
background-color: #f2f2f2;
padding: 20px;
}
flex: 3;
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
}
footer {
background-color: #333;
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My Flexbox Webpage</h1>
</header>
<a href="#">Home</a>
<a href="#">About</a>
<a href="#">Contact</a>
</nav>
<div class="sidebar">
<h2>Sidebar</h2>
<p>Links or other info
here.</p>
</div>
<h2>Main Content
Section</h2>
<p>This is the main content area
of the page.</p>
</section>
</div>
<p>© 2025 My Website. All
rights reserved.</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>








Comments
Post a Comment